ABS Injection Molding Material
What is ABS Material?
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent mechanical properties and ease of processing. It combines high impact resistance, toughness, and rigidity, making it ideal for a variety of applications. From a chemical and physical performance perspective, ABS plastic is safe under normal temperature and chemical conditions.
Chemical Analysis of ABS
- Acrylonitrile: This component provides ABS with chemical resistance and thermal stability. Its presence helps the polymer withstand various chemicals and maintain its properties at higher temperatures.
- Butadiene: Butadiene contributes significantly to the toughness and impact strength of ABS. It introduces rubbery characteristics, enhancing the material's ability to absorb impact and resist cracking.
- Styrene: Styrene adds rigidity and ease of processing to ABS. It allows the material to be easily molded into complex shapes with smooth surfaces and fine details.
These chemical characteristics make ABS an excellent choice for applications requiring a balance of durability, processability, and aesthetic qualities.

What are the advantage and disadvantages of ABS Plastics?
Advantages of ABS
- High Impact Resistance: ABS can withstand significant impact without cracking or breaking, making it ideal for durable applications.
- Good Toughness: It offers excellent toughness, providing a balance of rigidity and flexibility.
- Ease of Processing: ABS is easy to mold and can be processed at relatively low temperatures, allowing for detailed and complex shapes.
- Chemical Resistance: It has good resistance to acids and alkalis, enhancing its durability in various environments.
Disadvantages of ABS
- Weather Resistance: ABS has moderate weather resistance and is not suitable for prolonged exposure to extreme conditions without UV stabilization. ABS can become breakable and lose its color when exposed to outdoor elements for extended periods, which limits its suitability for long-term outdoor applications.
- Chemical Sensitivity: It is less resistant to organic solvents, which can cause degradation.
- Thermal Stability: While it offers decent thermal stability, ABS can deform under high temperatures, limiting its use in high-heat applications. It tends to melt and burn, releasing potentially toxic fumes.

ABS Material Properties
Before deciding whether to produce a part using ABS, we need to understand the part's operating environment, usage intensity, and purpose. Then, we can design the product's appearance and structure by considering the mechanical properties of ABS, such as shrinkage rate and tensile strength. Therefore, knowing the properties of ABS is a crucial step in the design process.
| Properties | Units | ASTM Test | ABS |
TENSILE STRENGTH | psi | D638 | 4100 |
FLEXURAL MODULUS OF ELASTICITY | psi | D790 | 304,000 |
TENSILE ELONGATION | % | D638 | 32 |
FLEXURAL STRENGTH | psi | D790 | 9,100 |
COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH | psi | D695 | - |
HARDNESS | scale as noted | D785,D2240 | R102 |
IZOD IMPACT(notched) | ft-lbs/in of | D256 | 7.7 |
HEAT DEFLECTION TEMPERATURE(66psi / 264psi) | F | D648 | 200 / 177 |
WATER ABSORPTION(Immersion 24 hours) | % | D570 | 0.3 |
SPECIFIC GRAVITY | - | D792 | 1.04 |
* Table value for ABS ( Source: CURBELL PLASTICS )
* ASTM TEST refers to standardized tests developed by ASTM International (American Society for Testing and Materials) to evaluate the properties and performance of materials. These tests provide consistent and reliable methods for measuring various mechanical, thermal, electrical, and other properties.
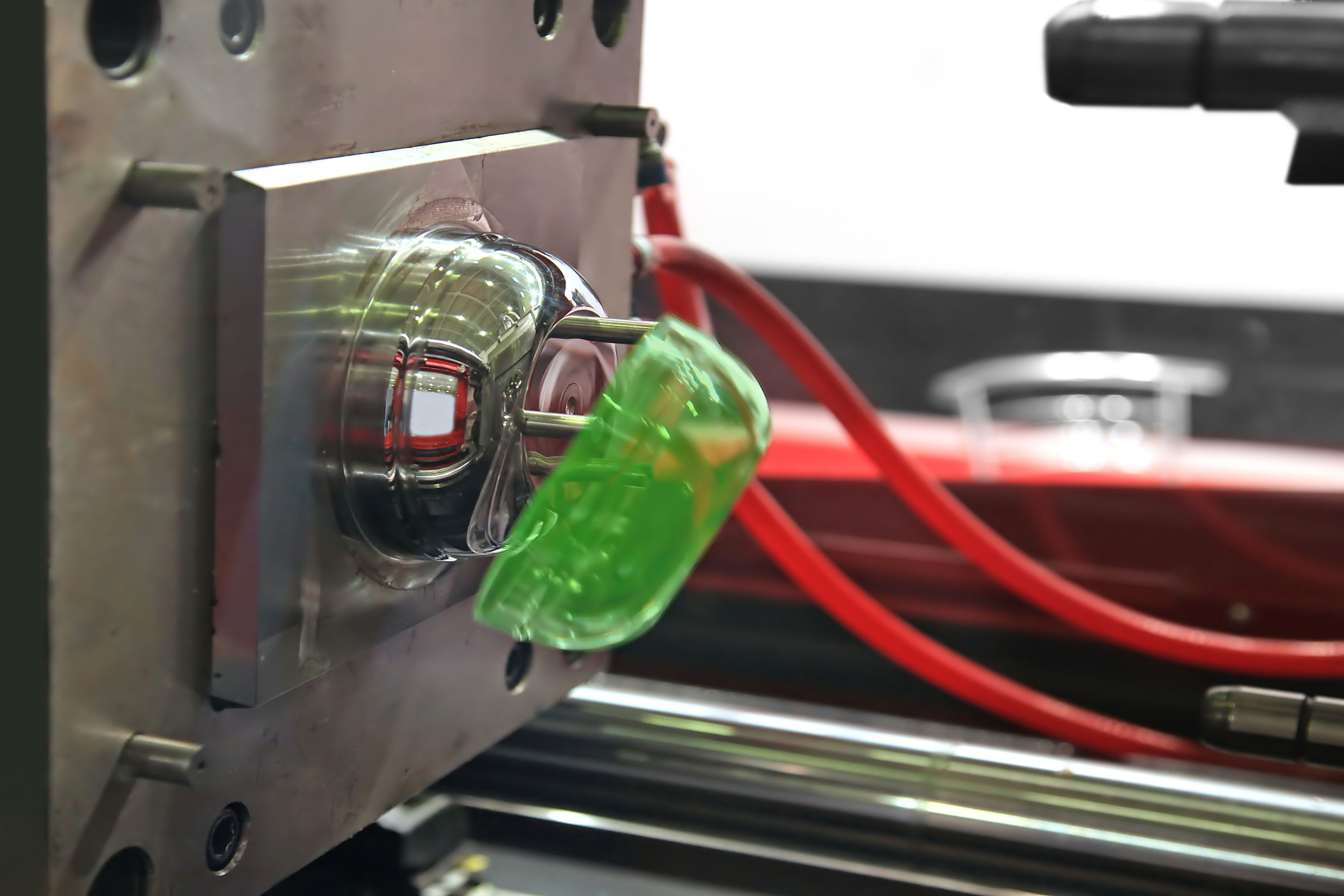
ABS Plastic Injection Molding
ABS is one of the most commonly used plastic materials due to its ease of production and processing. However, adhering to standard design guidelines is essential. At Ideal Pro, with over 30 years of injection molding experience, our Turnkey Solutions Service helps clients minimize and avoid challenges in product development. Here are some recommendations for the design and production process of ABS, which can serve as your reference.
Design Considerations for ABS Plastic:
| Keep wall thickness uniform to avoid warping and ensure consistent cooling. Typical thickness ranges from 1.5 to 4.5 mm. | |
Draft Angles | Include draft angles (1-2 degrees) in the design to facilitate easy ejection from the mold. | |
Ribs and Bosses | Use ribs and bosses to enhance structural integrity while minimizing material usage. Ribs should be about 50-60% of the wall thickness. | |
Fillets and Radii | Incorporate rounded corners and fillets to reduce stress concentrations and improve flow during molding. | |
Texturing | Consider texturing the surface to hide imperfections and improve the aesthetic appeal. | |
UV Protection | For outdoor products, use UV-stabilized ABS grades to prevent degradation. | |
Chemical Exposure | Ensure the design considers exposure to chemicals, avoiding solvents that can weaken the material. |
Injection Molding Consideration for ABS Plastic:
Processing Temperature | Ensure the material is heated between 200°C and 250°C for optimal flow and mold filling. |
Mold Temperature | Maintain mold temperatures between 40°C and 80°C to achieve good surface finish and dimensional stability. |
Injection Pressure | Use injection pressures ranging from 60 to 150 MPa to ensure proper mold filling and part integrity. |
Moisture Control | ABS is hygroscopic, so it must be dried thoroughly before processing to prevent defects like splay or bubbles. Typically, drying is done at 80°C for 2-4 hours. |
Shrinkage | Consider ABS's shrinkage rate of 0.4% to 0.7% when designing molds to ensure accurate dimensions of the final product. |
Taking a product from concept to successful market launch is a long and multifaceted journey. The success of this journey hinges on various factors, one of the most critical being the selection of materials and manufacturing processes. This consideration should ideally start at the initial design phase. Think of it like preparing a delicious meal: you first envision the desired taste, and then you choose the ingredients and cooking methods accordingly. There are many combinations and choices, but regardless of the combination (ingredients + cooking methods; materials + manufacturing processes), overall cost and context must be considered. Just as you wouldn't serve a hot dog at a fine dining event, you also wouldn't use expensive carbon fiber for the surface decoration of an economy product.
At Ideal Pro, our expert project consultants and engineers can help you find the perfect combination to ensure the success of your project. Our team possesses the skills and expertise necessary for everything from product design to prototyping and mass production. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Check out our past cases or contact us directly for advice and quotes.